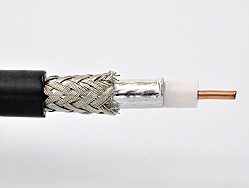
Triaxial cable
Triaxial cables, a special variant of coaxial cable, consist of three concentric conductors separated by a dielectric and a shield. This structure gives them improved performance and makes them an important tool in video technology and electrical measurement.
Triaxial cables are used in electrical measurement technology in particular, as they enable extremely precise measurements. The second outer conductor creates a small protective atmosphere so that even very low currents and signals can be measured without external electrical influences. Even currents in the femtoampere range can be measured, which is of crucial importance in many applications.
However, it is important to note that the processing of triaxial cables is generally more complex than conventional coaxial cables due to their more complex structure. This higher manufacturing effort is reflected in their technical performance and precision, making them a worthwhile investment for applications requiring the highest accuracy.
Triaxial cables are available in our online shop and also pre-assembled upon request. It is important that you tell us the exact signal distribution when you make your enquiry.
| Triaxial cable | Type | max. Freq. (GHz) | Attenuation at 2 GHz/m | Outer sheath | outer Ø (mm) | outer Ø (inch) | Article |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 017820 | 50 Ω | FEP | 2.80 | 0.11 | 050204 | ||
| 001101 | 50 Ω | PTFE | 3.40 | 0.134 | 050206 | ||
| TRX316 – RGT316 | 50 Ω | 2.5 | 1.23 | FEP | 3.60 | 0.142 | 050158 |
| 017910 | 75 Ω | FEP | 3.60 | 0.142 | 050205 | ||
| G_02330_HT | 50 Ω | 1 | PVC | 5.30 | 0.209 | 050174 | |
| G_02332 | 50 Ω | 2 | 1.45 | PVC | 4.25 | 0.167 | 050166 |
| RGT400 | 50 Ω | 2.5 | 0.79 | FEP | 5.70 | 0.224 | 050164 |
| Belden 9222 | 50 Ω | 1 | PVC | 6.10 | 0.24 | 050128 |
Simplified structure of a triaxial cable

- Inner conductor (completion as massive wire or litz wire (1b))
- Dielectric medium / Insulation
- Shield braiding or foil
- Dielectric medium / Insulation
- Shield braiding or foil
- Outer sheath
Due to the structure of the triaxial cable, it is easy to see that the connectors differ from those of the standard coaxial cable. For further information, please do not hesitate to contact us.