by Serviceteam | May 12, 2016 | Coaxial cable, Online-shop, Triaxial cable
A coaxial cable consists of two concentric conductors, which are seperated by a dielectric and by a screen. Fields of applocation for coaxial cables are video technology, electrical measurement as well as applications, where radio signals have to be transferred without loss.
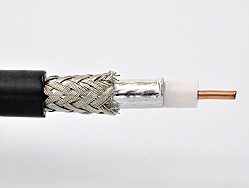
A double screened coaxial cable is presented here
Structure of a double screened coaxial cable:
1 = inner conductor – solid wire or stranded wires (1b)
2 = dielectric / isolation
3a = braid or foil
3b = braid or foil
4 = outer sheath
more information about the structure of such cables: Structure coaxial cable
The wave impedance is only depending on the outer diameter of the inner conductor, the inner diameter of the outer conductor and the dielectric constant of the intermediate dielectric. A vacuum is the best dielectric.
Question: Which is the right cable for my application?
For applications up to 1GHz we recommend the RG174, for applications up to 2.5GHz we recommend the RG179, RG188, RG187 or RG316. For applications above 2.5Ghz we recommend the use of low loss cable such as SS405, Multiflex_86 or CLF100. Due to the used materials and the cable structure, those cables are suitable for high frequencies (see illustration „Attenuation“).
Compare coaxial cables > technical specifications > Link

by Serviceteam | May 12, 2016 | Coaxial cable
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN COAXIAL CABLE AND NORMAL CABLE!
The conductor is isolated from the shielding by the dielectric and is located in the center of the cable. The geometry must be closely adhered. Is a coaxial cable bent lower than the permissible bending radius, the electrical values are no longer complied and the cable is no longer useful for specific application.
Information on the structure of coaxial cable: Structure coaxial cable

by Serviceteam | May 5, 2016 | Accessory, Cable assembly, Coaxial cable
Koaxialkabel 50 Ohm – Bildergalerien 1,5 – 2,1 mm / Gr:1
Koaxialkabel 50 Ohm – Bildergalerien 2,4 – 3,2 mm / Gr:2
Koaxialkabel 50 Ohm – Bildergalerien 3,2 – 4,2 mm / Gr:3
Koaxialkabel 50 Ohm – Bildergalerien 4,9 – 6,1 mm / Gr:4
Koaxialkabel 50 Ohm – Bildergalerien 6,9 – 7,9 mm / Gr:5
Koaxialkabel 50 Ohm – Bildergalerien 10,0 – 11,0mm / Gr:6
Koaxialkabel 50 Ohm – Bildergalerien 14,0 – 15,0mm / Gr:7

by Serviceteam | May 5, 2016 | Cable assembly, Cable configurator
Cable Assembly with our cable Configurator
Choose your best combination from over 100 different Plugs and Sockets, as well as over 100 different cable types. A large storage capacity allows a rapid manufacturing in Karlsruhe! You can use our interactive cable configurator based on images and associated information – order online and the cable can be with you the next day!

DIFFERENCE BETWEEN COAXIAL CABLE AND NORMAL CABLE!
The conductor is isolated from the shielding by the dielectric and is located in the center of the cable. The geometry must be closely adhered. Is a coaxial cable bent lower than the permissible bending radius, the electrical values are no longer complied and the cable is no longer useful for specific application.
Information on the structure of coaxial cable: Structure coaxial cable
by Serviceteam | Jan 9, 2015 | Cable assembly, Cable configurator, Coaxial cable, General
You want to compare two different coaxial cables?
Here you can see at first sight the characteristics of each coaxial cable, possibly from different manufacturers.
Question: Which is the right cable for my application?
For applications up to 1GHz we recommend the RG174, for applications up to 2.5GHz we recommend the RG179, RG188, RG187 or RG316. For applications above 2.5Ghz we recommend the use of low loss cable such as SS405, Multiflex_86 or CLF100. Due to the used materials and the cable structure, those cables are suitable for high frequencies (see illustration „Attenuation“).
Compare coaxial cables > technical specifications > Link